Saturday, October 31, 2020
Failed pleurodesis
A) ≥5 cm H2O per liter of fluid
B) ≥10 cm H2O per liter of fluid
C) ≥15 cm H2O per liter of fluid
D) ≥20 cm H2O per liter of fluid
E) ≥25 cm H2O per liter of fluid
Answer: D
Pleurodesis requires contact between two layers of a lung to be successful i.e., the visceral and parietal pleurae. Failed pleurodesis is a term applied if a lung failed to fully expand to the chest wall. Various causes include "trapped lung", interstitial pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or any kind of endobronchial obstruction. In such cases, failed pleurodesis appears as pneumothorax after the procedure. One of the way to predict a failed pleurodesis is using pleural manometry pressure during thoracentesis. Pleural pressure changes is a good surrogate of pleural elastance. A final value for pleural elastance ≥19-20 cm H2O per liter of fluid removed predicts a high likelihood of a failed pleurodesis.
#pulmonary
#procedures
References:
1. Doelken P, Huggins JT, Pastis NJ, Sahn SA. Pleural manometry: technique and clinical implications. Chest 2004; 126:1764.
2. Feller-Kopman D, Parker MJ, Schwartzstein RM. Assessment of pleural pressure in the evaluation of pleural effusions. Chest 2009; 135:201.
Friday, October 30, 2020
crossreactivity of contrasts
Q: 58 years old male is admitted to ICU due to Atrial Fibrillation associated Rapid Ventricular Rate (AF-RVR). Patient developed acute abdominal pain after a few hours of admission and requires CT scan with contrast. Patient has a previous history of allergies with shellfish and gadolinium contrast. Your next step of management? (select one)
A) Proceed with CT scan with IV contrast
B) 'Prep' patient with steroid & diphenhydramine
Answer: A
'CT scan with IV contrast' is an everyday affair in ICU. There are two objectives to this question. The first is to clarify the misconception that prophylactic 'preps' are needed in IV contrast for CT scan, in cases with hypersensitivity to other compounds including gadolinium contrast as well as shellfish, and topical povidone-iodine solutions. In actuality, in a strict sense, there is no such thing as "iodine allergy", a frequently used misterm. Iodine is a fundamental element in the human body.
The second objective of this case scenario is to emphasize learning the art of risk vs. benefit. In many situations like severe acute abdominal pain as in our patient with AF-RVR, it may be required to 'bite the bullet' and proceed to CT scan. Delay in many clinical situations may be detrimental to the patient.
#allergy-immunology
#radiology
References:
1. Macy EM. Current Epidemiology and Management of Radiocontrast-Associated Acute- and Delayed-Onset Hypersensitivity: A Review of the Literature. Perm J. 2018;22:17-072. doi:10.7812/TPP/17-072
2. Schabelman E, Witting M. The relationship of radiocontrast, iodine, and seafood allergies: a medical myth exposed. J Emerg Med 2010; 39:701.
3. Bottinor W, Polkampally P, Jovin I. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media. Int J Angiol. 2013;22(3):149-154. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1348885
Thursday, October 29, 2020
MG in pregnancy
Q; 32 years old female in the first trimester of pregnancy is admitted to ICU with exacerbation of her Myasthenia Gravis (MG). The patient is started on pyridostigmine. This patient might require? (select one)
A) higher dose
B) lower dose
Answer: A
Pyridostigmine i.e., acetylcholinesterase inhibitors stays the standard first-line treatment for MG in pregnancy. But, it may require a higher dose as renal clearance goes up in pregnancy, there is an expanded maternal blood volume, and frequent emesis. The important thing is to remember to decrease the interval of administration. Later, increase the dose if symptoms persist. Said that caution should be taken to avoid intravenous (IV) pyridostigmine just prior to delivery as it may cause uterine contractions.
#neurology
#ob-GYN
References:
1. Stafford IP, Dildy GA. Myasthenia gravis and pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2005; 48:48.Wednesday, October 28, 2020
Echodensity of mitral valve mass
Q: A low density of mechanical mitral valve mass on echocardiogram favors? (select one)
A) Thrombus
B) Pannus
Answer: A
Echodensity can be described in two ways:
1. Qualitatively -
- low intensity: similar to myocardial echodensity
- high-intensity: similar to the prosthetic hardware echodensity
2. Quantitatively -
It is described as using the ratio of the intensity of mass/intensity of prosthesis. A low-intensity mass of ≤0.45 suggests a presumptive diagnosis of thrombus.
#surgical-critical-care
#cardiology
References:
1. Barbetseas J, Nagueh SF, Pitsavos C, et al. Differentiating thrombus from pannus formation in obstructed mechanical prosthetic valves: an evaluation of clinical, transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic parameters. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998; 32:1410.
2. Lin SS, Tiong IY, Asher CR, et al. Prediction of thrombus-related mechanical prosthetic valve dysfunction using transesophageal echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86:1097.
Tuesday, October 27, 2020
Barbiturate coma - side effects
Q: Which of the following is NOT a side-effect of pentobarbital induced coma?
A) delay in brain death determination
B) need of vasopressor
C) aadynamic ileus
D) risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia
E) severe acidosis from ethylene-glycol toxicity
Answer: E
The induction of barbiturate coma is a common practice in neuro-surgical ICUs. In severe cases of high intracranial pressure (ICP), it helps in decreasing cerebral metabolic demand, Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF), and cerebral blood volume. Its infusion is monitored by continuous electroencephalography (EEG) monitoring, with the objective of a burst-suppression pattern. Barbiturate coma comes with its own price of various side-effects. Due to its very long half-life, there is frequently a delay in brain death determination. Hypotension is a norm and the need for pressor(s) is universal which may lead to arrhythmias as well as organs dysfunction. It also causes ileus. Poor mucus clearance increases the risk for ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). Pentobarbital is often prepared in propylene-glycol (not ethylene-glycol - choice E) and longer infusions may result in severe metabolic acidosis.
The objective of the above question is to highlight the dangers of iatrogenic propylene glycol toxicity in ICUs which is used as a diluent in many intravenous infusions including phenytoin, diazepam, and lorazepam besides pentobarbital.
#pharmacology
References:
1. Zosel A, Egelhoff E, Heard K. Severe lactic acidosis after an iatrogenic propylene glycol overdose. Pharmacotherapy. 2010;30(2):219. doi:10.1592/phco.30.2.219
2. Miller MA, Forni A, Yogaratnam D. Propylene glycol-induced lactic acidosis in a patient receiving continuous infusion pentobarbital. Ann Pharmacother 2008; 42:1502.
3. Roberts I, Sydenham E. Barbiturates for acute traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012; 12:CD000033.
4. Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XI. Anesthetics, analgesics, and sedatives. J Neurotrauma 2007; 24 Suppl 1:S71.
Monday, October 26, 2020
Vitamins in SIBO
Sunday, October 25, 2020
Ketamine
Q; In dissociative sedation, a patient retains the spontaneous respirations but not the airway protective reflexes? (select one)
A) True
B) False
Answer: B
Lately, Ketamine use is on increase as a sedative agent in ICUs across the USA. This is is due to its property of causing dissociative sedation. Due to this unique property patient may appear in a trance-like cataleptic state. Ketamine also provides good analgesia. It also causes amnesia. Despite these effects, a patient retains both spontaneous respirations and airway protective reflexes. This makes it useful in non intubated patients as a sedative-infusion or for use in procedural sedation. Ketamine also keeps hemodynamic stability.
#pharmacology
#sedation-analgesia
References:
1. Umunna BP, Tekwani K, Barounis D, Kettaneh N, Kulstad E. Ketamine for continuous sedation of mechanically ventilated patients. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2015;8(1):11-15. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.145414
2. Brown TB, Lovato LM, Parker D. Newton A, Fitton L. Intravenous ketamine for adult procedural sedation in the emergency department: a prospective cohort study. Emerg Med J 2008; 25:498.
3. Patrick M. Wieruszewski, PharmD; Jonathan G. Leung, PharmD, BCPS, BCPP; Sarah Nelson, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP Ketamine Use in the Intensive Care Unit AACN Adv Crit Care (2018) 29 (2): 101–106. https://doi.org/10.4037/aacnacc2018448Saturday, October 24, 2020
tuberculin test and sarcoid
Q: 34 years old female with a past medical history of sarcoidosis and recently immigrated from an epidemiological area with a high pulmonary tuberculosis rate is admitted to ICU with community-acquired pneumonia. CXR showed a cavitary lesion. Patient was recently tested negative for "skin TB test" at the workplace. Your next step of management?
A) Isolation
B) No isolation
Answer: A
Sarcoidosis doesn't provide a reliable skin reactivity test for the mycobacterial disease. It is not a good test to screen latent tuberculosis infection. In fact, a positive test is highly diagnostic of mycobacterial disease as sarcoidosis has diminished reactivity to TB (tuberculin) test. In other words, the tuberculin skin test has high specificity but poor sensitivity for tuberculosis in sarcoid patients.
#pulmonary
Reference:
Smith-Rohrberg D, Sharma SK. Tuberculin skin test among pulmonary sarcoidosis patients with and without tuberculosis: its utility for the screening of the two conditions in tuberculosis-endemic regions. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2006 Jun;23(2):130-4. PMID: 17937109.
Friday, October 23, 2020
Commotio cordis
Thursday, October 22, 2020
Tuberculous peritonitis
Q: 44 year old male with previous histories of AIDS, cirrhosis, diabetes, underlying Kaposi sarcoma, and renal failure (on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis - CAPD) is admitted in ICU with severe abdominal pain. Subsequent workup diagnosed him with tuberculous peritonitis. Which of his past medical history is the highest risk factor for tuberculous peritonitis?
A) cirrhosisB) peritoneal dialysis
C) diabetes mellitus
D) underlying malignancy
E) AIDS
Answer: A
One of the studies has shown the following factors in descending order as risk factors for tuberculous peritonitis. It may be hard to believe that AIDS is the lowest risk factor!
- cirrhosis,
- peritoneal dialysis
- diabetes mellitus
- underlying malignancy
- systemic corticosteroids, and
- AIDS
Wednesday, October 21, 2020
Index card test
Q: Q: What is 'card test' for extubation?
Answer: Cough strength is considered to be one of the most reliable indicators of successful extubation. Cough strength is usually evident with deep suctioning of the endotracheal tube (ETT). Experts have developed some formal tests and one of the formal tests is the 'card' test. It can be performed by detaching ETT and holding a simple index card at about 2 cm away from the ETT tip. If a patient cannot moisten the card on 3-4 attempts at cough, the likelihood of failed extubation is high.
#ventilators
Reference:
Khamiees M, Raju P, DeGirolamo A, et al. Predictors of extubation outcome in patients who have successfully completed a spontaneous breathing trial. Chest 2001; 120:1262.
Tuesday, October 20, 2020
Factors in UGI bleed
Q: Which of the following is likely to be present in upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleed? (select one)
A) blood urea nitrogen to serum creatinine ratio > 20
B) blood urea nitrogen to serum creatinine ratio > 30
Answer: B
Predictive factors for a UGI bleed can be described in Likelihood ratios (LR). Some of the important factors with their LR are below:
- patient's history of melena (LR 5.1-5.9)
- melenic stool on examination (LR 25)
- blood or coffee-ground material on nasogastric (NG) lavage (LR 9.6)
- ratio of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) to serum creatinine (Cr) > 30 (LR 7.5)
- tachycardia (LR 4.9)
- hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL (LR 4.5-6.2)
Monday, October 19, 2020
Ppl on vent
Q: The plateau pressure (Pplat or Ppl) on a ventilator is a reflection of static compliance of? (select one)
A) lung parenchyma
B) chest wall
C) chest wall and abdomen
D) Lung parenchyma, chest wall and abdomen
Answer: D
The objective of the above question is to emphasize the role of abdominal pressure during ventilation. Excessive focus on the chest/thoracic-cage may keep clinicians away from considering a major role high intraabdominal pressure (IAP) plays in chest mechanics or failed ventilation. Reading Pplat in conjunction with a physical exam, other ventilator parameters, and radiological findings may help in solving this query.
Unfortunately, there is a dearth of recent literature on this topic, we tried to put some articles together in the reference section.
# ventilators
#pulmonary
References:
1. Richardson JD, Trinkee JK. Hemodynamic and respiratory alterations with increased intra-abdominal pressure. J Surg. 1976;20:401–4.
2. Ridings PC, Bloomfield GL, Blocher GR, Sugerman HJ. Cardiopulmonary effects of raised intra-abdominal pressure before and after intravascular volume expansion. J Trauma. 1995;39:1071–5.
3. Cullen DJ, Coyle JP, Teplick R, Long MC. Cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal effects of massively increased intra-abdominal pressure in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 1989;17:118–21.
4. Bloomfield GL, Ridings PC, Blocher CR, Marmaru A, Sugerman HJ. A proposed relationship between increased intra-abdominal, intrathoracic, and intracranial pressure. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:496–503.
5. Pelosi P, Cereda M, Foti G, Giacomini M, Pesenti A. Alterations of lung and chest wall mechanics in patients with acute lung injury: effects of positive end-expiratory pressure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:531–7.
6. Malbrain ML, Deeren D, Nieuwendiijk R. Partitioning of respiratory mechanics in intra-abdominal hypertension. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:S85.
7. Anbar JT, Antunes T, Barbas CSV. Influence of PEEP and external abdominal weight in airway and intra-abdominal pressures in mechanically ventilated ICU patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. p. A665.
8. Mutoh T, Lamm WJ, Embree LJ, Hildebrandt J, Albert RK. Abdominal distension alters regional pleural pressures and chest wall mechanics in pigs in vivo. J Appl Physiology. 1991;70:2611–8
9. Tobin MJ. Respiratory monitoring. JAMA 1990; 264:244.Sunday, October 18, 2020
clonidine
Q: Describe at least five uses of clonidine besides its use in the treatment of hypertension (HTN)?
Answer: Although Clonidine's main indication is HTN, it has been used successfully (mostly off-label) in many other situations such as
- adjunctive anesthetic sedation and analgesia
- spinal anesthesia
- opioid detoxification
- alcohol withdrawal
- smoking cessation
- postmenopausal hot flashes
- attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity
- refractory conduct disorder
- sleep disturbances in children
Saturday, October 17, 2020
TOF
Q: 72 years old male with previous history of HTN, DM, CAD, previous CABG, alcoholism, and stroke (with some residual hemiplegia on the left side) is admitted with ARDS secondary to severe pancreatitis. Dure to high asynchrony with ventilator, patient required neuromuscular blockade (NMB) along with sedation and analgesia. Which one precaution is required during the application of Train of Four (TOF)?
Answer: Train of Four (TOF) should be avoided on the paralyzed extremity.
The train of four (TOF) responses, described as T4/T1 ratio are usually exaggerated in paralyzed extremities. In patients who have a previous history of stroke, there is an upregulation of acetylcholine receptors after denervation on the paralyzed limbs. This results in resistance to nondepolarizing NMB agents. The application of TOF gives variable exaggeration of its ratio. This leads to an underestimation of the degree of systemic neuromuscular blocker.
#neurology
References:
1. Moningi, Srilata MD; Durga, Padmaja MD, DNB, PDCC; Mantha, Srinivas MD; Ramachandra, Gopinath MD, FFARCSI, DA Train of Four Responses in Paretic Limbs, Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology: October 2009 - Volume 21 - Issue 4 - p 334-338 doi: 10.1097/ANA.0b013e3181ad4b37
2. Iwasaki H, Namiki A, Omote K, et al. Response differences of paretic and healthy extremities to pancuronium and neostigmine in hemiplegic patients. Anesth Analg 1985; 64:864.
Friday, October 16, 2020
Eye exam on trauma
Case: 24 year old female is brought to the trauma Emergency room (ER) after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). She mostly received facial injuries while in the back seat without a seat belt. Patient has no past medical history (PMH) except cosmetic Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK) on her eyes 3 years ago. Patient is complaining of decrease vision and feels something is in her eye. There are also lacerations on both eyelids and requiring pressure to hold the bleeding. What would be your next step?
Answer: Call for an emergent ophthalmic consult
The objective of the above question is to emphasize that the intraocular injuries take precedence over external injuries such as eyelids or canalicular lacerations. Patients with any prior procedures to eyes such as LASIK or cataract surgery increase the risk of an occult rupture, particularly if they complain of decreased visual acuity.
In case of previous LASIK disruption of the corneal flap may occur and may be visible on an exam. An emergent ophthalmologic consult is required.
#trauma
Reference:
Tsai TH, Peng KL, Lin CJ. Traumatic corneal flap displacement after laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) [published correction appears in Int Med Case Rep J. 2017 Jul 26;10 :261]. Int Med Case Rep J. 2017;10:143-148. Published 2017 Apr 19. doi:10.2147/IMCRJ.S128637
Thursday, October 15, 2020
electrolytes in SJS/TEN
Q: Which two electrolytes are considered a good marker of disease severity in Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)?
Answer: Serum urea nitrogen and glucose
Contrary to popular belief, eosinophilia is unusual in SJS/TEN. Neutropenia is considered a marker for poor prognosis but it is hard to predict as the administration of steroids obscure neutropenia due to demarginalization and mobilization of neutrophils into the circulation.
When it comes to electrolytes, serum urea nitrogen above 28 mg/dL and glucose above 250 mg/dL are considered good markers of disease severity.
#electrolytes
#dermatology
#pharmacology
References:
1. Westly ED, Wechsler HL. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Granulocytic leukopenia as a prognostic indicator. Arch Dermatol 1984; 120:721.
2. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, et al. SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 115:149.
Wednesday, October 14, 2020
optimum platelet count for procedures
Tuesday, October 13, 2020
TCD and brain death
Monday, October 12, 2020
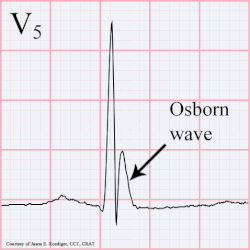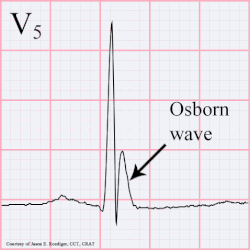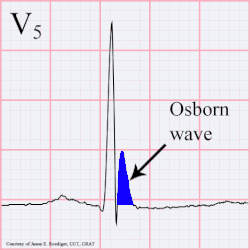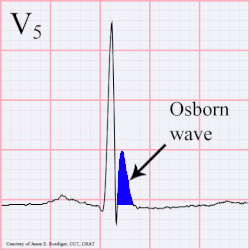
osborn wave
Osborn wave on EKG, which is usually a hallmark of hypothermia - and manifest around 32 C / 90 F is due to serum hypercalcemia. It can manifest in any other conditions with hypercalcemia due any other disease pathology. They have also been described after strokes.
Sunday, October 11, 2020
pneumothorax ex vacuo
Q: What is Pneumothorax ex vacuo?
Answer: Pneumothorax ex vacuo can be called a misnomer. It is formed when after thoracentesis the lung stays trapped due to thick fibrous pleural rind, cannot expand, and air filled the space. The exacerbating factor in this phenomenon is the negative pleural pressure created during the procedure. This may pull the air through the track formed by the catheter. Thick fibrous pleural rind may formed due to chronic underlying disease such as atelectasis, bronchial obstruction, an inflammatory or malignant process.
#pulmonary
#procedures
References:
1. Woodring JH, Baker MD, Stark P. Pneumothorax ex vacuo. Chest 1996; 110:1102.
2. Byrd RP Jr, Roy TM. Pneumothorax ex vacuo. Chest. 1997 Jul;112(1):293-4. doi: 10.1378/chest.112.1.293-a.
Saturday, October 10, 2020
Arterial and venous blood culture
Q: Venous blood cultures tend to get more contaminated than arterial blood cultures?
A) True
B) False
Answer: False
We were able to find only one small study of 51 patients in the literature which is more than three decades old. So although the evidence is weak, blood cultures obtained either via veins or arteries have the same yield. Said that it does not justify obtaining the blood cultures from the freshly placed arterial lines just for the sake of ease. Blood cultures obtained via catheters have an extremely high ratio (OR=2.69) of being contaminated. This includes freshly placed catheters. If there is no contra-indication, blood cultures should always be obtained through fresh venipuncture, preferably from upper extremity blood vessels.
#infectious-diseases
#procedures
References:
1. Väisänen IT, Michelsen T, Valtonen V, Mäkeläinen A. Comparison of arterial and venous blood samples for the diagnosis of bacteremia in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 1985; 13:664.
2. Snyder SR, Favoretto AM, Baetz RA, et al. Effectiveness of practices to reduce blood culture contamination: a Laboratory Medicine Best Practices systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biochem 2012; 45:999.
Friday, October 9, 2020
PV and pregnancy
Q: 32 year old female with a past medical history of Polycythemia Vera (PV) is admitted to ICU after a complication in her first pregnancy with abruptio placentae. You should inform the patient that pregnancy is highly contraindicated in PV? (select one)
A) True
B) False
Answer: B
Despite an increased risk of complications in pregnancy such as miscarriages, abruptio placentae, pre-eclampsia, and intrauterine growth retardation, pregnancy is not a contraindication in patients with PV. A low dose aspirin decreases the rate of pregnancy loss. Patients should be closely monitored throughout the pregnancy. The European LeukemiaNet recommends the target hematocrit either less than 45% or the normal midgestation hematocrit range, whichever is lower. If cytoreduction is needed Interferon alfa is the preferred agent in pregnant women with PV.
#Ob-gyn
#hematology-oncology
References:
1. Barbui T, Barosi G, Birgegard G, et al. Philadelphia-negative classical myeloproliferative neoplasms: critical concepts and management recommendations from European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29:761.
2. Aggarwal N, Chopra S, Suri V, et al. Polycythemia vera and pregnancy: experience of four pregnancies in a single patient. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2011; 283:393.
3. Maze D, Kazi S, Gupta V, et al. Association of Treatments for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms During Pregnancy With Birth Rates and Maternal Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2019; 2:e1912666.
Thursday, October 8, 2020
"Basedow paraplegia"
Q: What is "Basedow paraplegia"?
Answer: "Basedow paraplegia" is an unusual acute neurological presentation of thyroid storm or in patients with severe hyperthyroidism. The classic presentation is an acute and severe weakness of lower extremities associated with areflexia. Upper extremities though get weak but usually less affected. It is hard to make diagnoses as clinical features may resemble Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) which may also occur in severe hyperthyroidism. Treatment is to manage the underlying thyroid pathology.
#endocrinology
#neurology
References:
1. Feibel JH, Campa JF. Thyrotoxic neuropathy (Basedow's paraplegia). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1976; 39:491.
2. Pandit L, Shankar SK, Gayathri N, Pandit A. Acute thyrotoxic neuropathy--Basedow's paraplegia revisited. J Neurol Sci 1998; 155:211.
Wednesday, October 7, 2020
Getting Sputum culture
Q: Asking a patient to rinse the mouth prior to obtaining sputum culture increases the optimal yield of the collected material? (select one)
A) True
B) False
Answer: A
A large number of pneumonia patients (almost one-third) cannot produce enough or right sputum specimens, even when they are asked to do under medical supervision. The four best way to increase the optimum yield and improve the quality of the specimen is:
- Getting sputum before starting antibiotic treatment
- Asking a patient to rinse the mouth before expectoration
- NPO couple of hours before expectoration
- Inoculate the culture media as soon as quickly preferably at the bedside
1. Muzanye G, Morgan K, Johnson J, Mayanja-Kizza H. Impact of mouth rinsing before sputum collection on culture contamination. Afr Health Sci. 2009;9(3):200.
2. Bartlett JG, Mundy LM. Community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:1618.Tuesday, October 6, 2020
psychosis in PD
Q: 72 year old male with past medical history of Parkinson's Disease (PD) is admitted to ICU with severe psychosis and tendency of hurting himself or others. What are the usual characteristics of severe psychosis in PD?
Answer: Visual hallucinations is the most common psychotic symptom in PD. Unfortunately, it is mostly due to Anti PD drugs. An interesting feature is that patients are mostly cognizant of the fact that their hallucinations are not real. Also, underlying Lewy body disease needs to be ruled out. The second symptom is delusion. Majorly described delusions are spousal infidelity, people stealing money, intruders living in the house, or nurses planning harmful plots.
#psychiatry
#neurology
References:
1. Aarsland D, Brønnick K, Ehrt U, et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease and dementia: frequency, profile and associated care giver stress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2007; 78:36.
2. Goetz CG, Wuu J, Curgian LM, Leurgans S. Hallucinations and sleep disorders in PD: six-year prospective longitudinal study. Neurology 2005; 64:81.
3. Fénelon G, Mahieux F, Huon R, Ziégler M. Hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain 2000; 123 ( Pt 4):733.
4. Sanchez-Ramos JR, Ortoll R, Paulson GW. Visual hallucinations associated with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 1996; 53:1265.
Monday, October 5, 2020
effects of IABP
Q: Intra Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) tends to _____________ the systolic blood pressure? (select one)
A) increase
B) decrease
Answer: B
Inflation of IABP during the heart's diastole displaces the blood to the proximal aorta. And, aortic volume is reduced during systole due to a vacuum effect by rapid balloon deflation (decrease afterload). These two actions result in a decrease in systolic blood pressure, an increase in diastolic blood pressure, and an increase in mean arterial pressure (MAP).
All these changes depend on arterial elastance. The higher the arterial elastance, the better the hemodynamic improvement response.
#hemodynamic
Reference:
1. Marchionni N, Fumagalli S, Baldereschi G, et al. Effective arterial elastance and the hemodynamic effects of intraaortic balloon counterpulsation in patients with coronary heart disease. Am Heart J 1998; 135:855.
2. Fried JA, Nair A, Takeda K, Clerkin K, Topkara VK, Masoumi A, Yuzefpolskaya M, Takayama H, Naka Y, Burkhoff D, Kirtane A, Karmpaliotis D, Moses J, Colombo PC, Garan AR. Clinical and hemodynamic effects of intra-aortic balloon pump therapy in chronic heart failure patients with cardiogenic shock. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2018 Nov;37(11):1313-1321. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Mar 20. PMID: 29678608; PMCID: PMC6148415.
Sunday, October 4, 2020
Prior use of inhaled glucocorticoids in COPD or asthma patients and parapneumonic effusions
Q: Prior use of inhaled glucocorticoids in COPD or asthma patients ___________ the chance of parapneumonic effusions? (select one)
Saturday, October 3, 2020
Destruction of RBC
Q: What percentage of total circulating Red Blood Cells (RBCs) get destruct per day?
Answer: 1%
The basic knowledge of RBC production, destruction, and survival is important while dealing with a patient with acute or chronic anemia. This becomes important when patients stay in ICU for a longer period of time and require blood draws every day.
The formula for RBC turnover rate is
RBC turnover rate (percent/day) = 100 ÷ RBC survival (days)
In a normal healthy adult, the normal RBC turnover rate is about a percent a day. And, in acute situations, the maximal sustainable capacity of the bone marrow to increase RBC production in an average healthy adult goes high up to 5 percent per day. In children, this turnover can go up to 8 percent in a stressful situation.
#hematology
References:
1. Smith JA. Exercise, training and red blood cell turnover. Sports Med. 1995;19(1):9-31. doi:10.2165/00007256-199519010-00002
2. Poyart C, Wajcman H. Hemolytic anemias due to hemoglobinopathies. Mol Aspects Med 1996; 17:129.
3. Handelman GJ, Levin NW. Red cell survival: relevance and mechanism involved. J Ren Nutr. 2010 Sep;20(5 Suppl):S84-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2010.06.007.
Friday, October 2, 2020
Contrast use in ICU
A) Yes
B) No
Answer: B
The objective of the above question is to highlight the common practice in ICU of ordering contrasts with radiological studies, leading to contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN). For most of the bone Magnetic Resonance Imagings (MRIs), IV contrast is not needed unless bone tumor or abscess is suspected. Arthrography of the shoulder requires percutaneous contrast. Ideally, it should be performed under fluoroscopy or ultrasound for proper needle placement. Extravasation of contrast is consistent with a full-thickness rotator cuff tear.
#orthopedic
#trauma
#nephrology
References:
1. Opsha O, Malik A, Baltazar R, et al. MRI of the rotator cuff and internal derangement. Eur J Radiol 2008; 68:36.
2. Lungu E, Moser TP. A practical guide for performing arthrography under fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance. Insights Imaging. 2015;6(6):601-610. doi:10.1007/s13244-015-0442-9
Thursday, October 1, 2020
blood oxygenation during VV ECMO
Q; What is the good determinant of adequate blood oxygenation in a patient on Veno-venous (VV) Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)?
Answer:
It can be easily estimated by knowing the ECMO Blood Flow/Cardiac Output Ratio. Any value above 60% provides adequate blood oxygenation.