Q: All of the following should be discontinued in severe ulcerative colitis (UC) except?
A) Anticholinergic drugs
B) Antidiarrheal agent
C) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
D) Narcotics/opioid drugs
E) Enteral nutrition
Answer: E
The objective of the above question is to emphasize the importance of the continuation of enteral nutrition in severe UC. Holding off enteral nutrition in severe UC may harm the patient. Enteral nutrition should hold off only in fulminant disease. Enteral nutrition provides colon short-chain fatty acids needed for the repair of colon epithelial cells.
All of the other choices can lead to toxic megacolon and should be discontinued.
#gastroenterology
#nutrition
References:
1. González-Huix F, Fernández-Bañares F, Esteve-Comas M, et al. Enteral versus parenteral nutrition as adjunct therapy in acute ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88:227.
2. Roediger WE. The starved colon--diminished mucosal nutrition, diminished absorption, and colitis. Dis Colon Rectum 1990; 33:858.
Wednesday, October 31, 2018
Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Tuesday, October 30, 2018
6 components of SOFA score
Q: Which component of coagulation profile is part of SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) score?
A) PT
B) PTT
C) Platelets
D) D-Dimer
E) Fibrinogen level
Answer: C
SOFA score is one of many scoring systems used to calculate a patient's status during the stay in an intensive care unit (ICU). The SOFA score is based on six different scores, one each for the respiratory, cardiovascular, hepatic, coagulation, renal and neurological systems. Scores less than 9 give predictive mortality at 33% while above 11 can be close to or above 95%.
Clinically, it is used to predict the risk of mortality before instituting aggressive treatment plans like ECMO. It is found to be superior to various other scores specific for various disease processes.
It can be accessed from any search engine on the internet.
#scores
Reference:
1. Vincent JL, de Mendonça A, Cantraine F, et al. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on "sepsis-related problems" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit Care Med 1998; 26:1793.
A) PT
B) PTT
C) Platelets
D) D-Dimer
E) Fibrinogen level
Answer: C
SOFA score is one of many scoring systems used to calculate a patient's status during the stay in an intensive care unit (ICU). The SOFA score is based on six different scores, one each for the respiratory, cardiovascular, hepatic, coagulation, renal and neurological systems. Scores less than 9 give predictive mortality at 33% while above 11 can be close to or above 95%.
- Respiratory system - P/F ratio
- Cardiovascular system - the need of vasopressors
- Hepatic system – the bilirubin level
- Coagulation system – the platelet count
- Neurologic system – the Glasgow coma score
- Renal system – the serum creatinine or urine output
Clinically, it is used to predict the risk of mortality before instituting aggressive treatment plans like ECMO. It is found to be superior to various other scores specific for various disease processes.
It can be accessed from any search engine on the internet.
#scores
Reference:
1. Vincent JL, de Mendonça A, Cantraine F, et al. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on "sepsis-related problems" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit Care Med 1998; 26:1793.
Monday, October 29, 2018
Overlapping of coronary stents
Q: In long coronary artery lesion, overlapping of drug-eluting stents (DES) decreases the rate of re-stenosis? (select one)
A) True
B) False
Answer: False
Unfortunately and defying the logic, the use of multiple overlapping DES, which may be required for longer lesions in coronary vessel are associated with more chances of re-stenosis. Different explanations have been proposed including drug toxicity, polymer instability in the overlapping segments, persistent inflammation or delayed reendothelialization at the overlapping sites. But still, it may be the treatment of choice in such situations, given risk vs benefit.
#cardiology
#procedures
References:
1. Kereiakes DJ, Wang H, Popma JJ, et al. Periprocedural and late consequences of overlapping Cypher sirolimus-eluting stents: pooled analysis of five clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 48:21.
2. Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Harnek J, et al. Differential response of delayed healing and persistent inflammation at sites of overlapping sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 2005; 112:270.
A) True
B) False
Answer: False
Unfortunately and defying the logic, the use of multiple overlapping DES, which may be required for longer lesions in coronary vessel are associated with more chances of re-stenosis. Different explanations have been proposed including drug toxicity, polymer instability in the overlapping segments, persistent inflammation or delayed reendothelialization at the overlapping sites. But still, it may be the treatment of choice in such situations, given risk vs benefit.
#cardiology
#procedures
References:
1. Kereiakes DJ, Wang H, Popma JJ, et al. Periprocedural and late consequences of overlapping Cypher sirolimus-eluting stents: pooled analysis of five clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 48:21.
2. Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Harnek J, et al. Differential response of delayed healing and persistent inflammation at sites of overlapping sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 2005; 112:270.
Sunday, October 28, 2018
Diagnosing Cerebral Malaria through Retina
Q: Which of the following retinal features is specific of cerebral malaria and can actually be diagnostic?
A) blurred disc margins
B) papilloedema
C) retinal hemorrhages
D) retinal whitening
E) retinal edema
Answer: D
Retina provides a unique opportunity to observe clues to the diagnosis of cerebral malaria. In fact, the detection of malarial retinopathy can be diagnostic for cerebral malaria, as set of retinal abnormalities are unique to cerebral malaria. These abnormalities include blurred disc margins, papilloedema, retinal hemorrhages, retinal whitening, retinal edema, vascular changes and soft exudates. Of these retinal whitening and vascular changes are specific to cerebral malaria.
#opthalmology
#infectiousdiseases
References:
1. Pedrosa CA, Santos C, Coutinho I, et al. Ophthalmologic identification of cerebral malaria in adults. GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2015;5:Doc13. Published 2015 Nov 2.
2. Beare NA, Lewallen S, Taylor TE, Molyneux ME. Redefining cerebral malaria by including malaria retinopathy. Future Microbiol. 2011 Mar;6(3):349–355.
3. Maude RJ, Dondorp AM, Abu Sayeed A, Day NP, White NJ, Beare NA. The eye in cerebral malaria: what can it teach us? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009 Jul;103(7):661–664.
A) blurred disc margins
B) papilloedema
C) retinal hemorrhages
D) retinal whitening
E) retinal edema
Answer: D
Retina provides a unique opportunity to observe clues to the diagnosis of cerebral malaria. In fact, the detection of malarial retinopathy can be diagnostic for cerebral malaria, as set of retinal abnormalities are unique to cerebral malaria. These abnormalities include blurred disc margins, papilloedema, retinal hemorrhages, retinal whitening, retinal edema, vascular changes and soft exudates. Of these retinal whitening and vascular changes are specific to cerebral malaria.
#opthalmology
#infectiousdiseases
References:
1. Pedrosa CA, Santos C, Coutinho I, et al. Ophthalmologic identification of cerebral malaria in adults. GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2015;5:Doc13. Published 2015 Nov 2.
2. Beare NA, Lewallen S, Taylor TE, Molyneux ME. Redefining cerebral malaria by including malaria retinopathy. Future Microbiol. 2011 Mar;6(3):349–355.
3. Maude RJ, Dondorp AM, Abu Sayeed A, Day NP, White NJ, Beare NA. The eye in cerebral malaria: what can it teach us? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009 Jul;103(7):661–664.
Saturday, October 27, 2018
Bronchopleural fistula closure
Q: In patients with Broncho-pleural Fistula (BPF), if treatment via interventional bronchoscopy is taken, what is the cutoff point to use devices instead of only occlusive materials?
A) BPF ≥ 3 mm
B) BPF ≥ 5 mm
C) BPF ≥ 8 mm
D) BPF at the proximal level
E) C and D
Answer: E
When it comes to treating BPF via interventional bronchoscopy, there are two criteria to decide between using occlusive materials or devices such as stents, Amplatzer devices or combining them with sealants is
#interventional-pulmonary
References:
1. Hollaus PH, Lax F, Janakiev D, et al. Endoscopic treatment of postoperative bronchopleural fistula: experience with 45 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 1998; 66:923.
2. Hartmann W, Rausch V. New therapeutic application of the fiberoptic bronchoscope. Chest 1977; 71:237.
A) BPF ≥ 3 mm
B) BPF ≥ 5 mm
C) BPF ≥ 8 mm
D) BPF at the proximal level
E) C and D
Answer: E
When it comes to treating BPF via interventional bronchoscopy, there are two criteria to decide between using occlusive materials or devices such as stents, Amplatzer devices or combining them with sealants is
- BPF ≥8 mm, and/or
- proximal fistulas (level of a major bronchus)
#interventional-pulmonary
References:
1. Hollaus PH, Lax F, Janakiev D, et al. Endoscopic treatment of postoperative bronchopleural fistula: experience with 45 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 1998; 66:923.
2. Hartmann W, Rausch V. New therapeutic application of the fiberoptic bronchoscope. Chest 1977; 71:237.
Friday, October 26, 2018
Open book fracture
Q: Open book fracture occurs at which part of the body?
Answer: Pelvis
Open book fracture is a kind of pelvic fracture associated with a heavy impact on the pubis, commonly seen after MVA (Motor Vehicle Accident). The left and right halves of the pelvis are separated at front and rear, the front opening more than the rear, i.e. like opening a book.
#trauma
References:
1. Grotz MR, Allami MK, Harwood P, et al. Open pelvic fractures: Epidemiology, current concepts of management and outcome. Injury. 2005;36(1):1–13.
2. Dente CJ, Feliciano DV, Rozycki GS, et al. The outcome of open pelvic fractures in the modern era. Am J Surg. 2005;190(6):830–835.
Answer: Pelvis
Open book fracture is a kind of pelvic fracture associated with a heavy impact on the pubis, commonly seen after MVA (Motor Vehicle Accident). The left and right halves of the pelvis are separated at front and rear, the front opening more than the rear, i.e. like opening a book.
#trauma
References:
1. Grotz MR, Allami MK, Harwood P, et al. Open pelvic fractures: Epidemiology, current concepts of management and outcome. Injury. 2005;36(1):1–13.
2. Dente CJ, Feliciano DV, Rozycki GS, et al. The outcome of open pelvic fractures in the modern era. Am J Surg. 2005;190(6):830–835.
Thursday, October 25, 2018
Tracheostomy tube tie
Q: What is the rule of thumb while applying tie to Tracheostomy tube?
Answer: “tight enough to slip one finger beneath the tie.”
The tie around tracheostomy tube must be tight enough to secure the tube but loose enough to avoid skin breakdown and vascular obstruction.
#procedures
#procedures
Sherman JM, Davis S, Albamonte-Petrick S, Chatburn RL, Fitton C, Green C, Johnston J, et al. Care of the child with a chronic tracheostomy: official statement of the American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161(1):297-308.
Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis
Q: Patients with severe pancreatitis are at increased risk for abdominal compartment syndrome due to?
A) aggressive fluid resuscitation
B) peripancreatic inflammation
C) ascites
D) ileus
E) all of the above
Answer: E
The objective of the above question is to highlight a much-ignored consequence of acute pancreatitis. Abdominal compartment syndrome can be devastating and instantly life-threatening if not addressed. A very low threshold should be kept to monitor bladder pressure with any indication of the clinical sign.
#gastroenterology
#surgicalcriticalcare
Reference:
Radenkovic DV, Bajec D, Ivancevic N, et al. Decompressive laparotomy with temporary abdominal closure versus percutaneous puncture with placement of abdominal catheter in patients with abdominal compartment syndrome during acute pancreatitis: background and design of multicenter, randomised, controlled study. BMC Surg 2010; 10:22.
A) aggressive fluid resuscitation
B) peripancreatic inflammation
C) ascites
D) ileus
E) all of the above
Answer: E
The objective of the above question is to highlight a much-ignored consequence of acute pancreatitis. Abdominal compartment syndrome can be devastating and instantly life-threatening if not addressed. A very low threshold should be kept to monitor bladder pressure with any indication of the clinical sign.
#gastroenterology
#surgicalcriticalcare
Reference:
Radenkovic DV, Bajec D, Ivancevic N, et al. Decompressive laparotomy with temporary abdominal closure versus percutaneous puncture with placement of abdominal catheter in patients with abdominal compartment syndrome during acute pancreatitis: background and design of multicenter, randomised, controlled study. BMC Surg 2010; 10:22.
Labels:
Gastroenterology,
surgical critical care
Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Mount Fuji Sign
Q: What is Mount Fuji Sign?
Answer: A sign in massive pneumocephalus
A massive accumulation of air compressing the frontal lobes is called the Mount Fuji sign.
Pneumocephalus can occur after neurosurgical procedures, after trauma or spontaneously. Small amounts of air usually reabsorbed but tension pneumocephalus may occur leading to life-threatening situations.
The CT finding resembles the silhouette of a volcano, such as Mount Fuji. A “peaking” sign is also indicative of increased tension and occurs when the frontal lobes form a peak in the midline on account of intact bridging veins.
Please click on the link (in reference) to see the picture and a case report#neurology
Reference:
Josef G. Heckmann, M.D., and Oliver Ganslandt, M.D. The Mount Fuji Sign. N Engl J Med 2004; 350:1881. April 29, 2004
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm020479
Monday, October 22, 2018
AMPLE in Trauma
Q: What does AMPLE stand for in Trauma?
Answer: AMPLE is the mnemonic to the standard trauma history
AMPLE has also been taught as SAMPLE by the addition of signs and symptoms at the beginning of the mnemonic.
#trauma
References:
1. Ed Dickinson; Dan Limmer; O'Keefe, Michael F.; Grant, Harvey D.; Bob Murray (2008). Emergency Care (11th Edition). Englewood Cliffs, N.J: Prentice Hall. p. 242.
2. Marx, J (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice 7th edition. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 267.
Answer: AMPLE is the mnemonic to the standard trauma history
- Allergies
- Medications (particularly anti-coagulants)
- Past history
- Last meal
- Events
AMPLE has also been taught as SAMPLE by the addition of signs and symptoms at the beginning of the mnemonic.
#trauma
References:
1. Ed Dickinson; Dan Limmer; O'Keefe, Michael F.; Grant, Harvey D.; Bob Murray (2008). Emergency Care (11th Edition). Englewood Cliffs, N.J: Prentice Hall. p. 242.
2. Marx, J (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice 7th edition. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 267.
Sunday, October 21, 2018
Naclerio's sign
Q: What is the most common anatomical site for Oesophageal rupture (Boerhaave's syndrome)?
Answer:
The most common tear in Boerhaave syndrome is at the left posterolateral wall of the lower third of the esophagus, 2–3 cm proximal to the stomach. Tears are vertically oriented, 1-4 cm in length.
On CXR it is called Naclerio's sign as a V-shaped air collection. One limb of the V is produced by mediastinal air outlining the left lower lateral mediastinal border. The other limb is produced by air between the parietal pleura and medial left hemidiaphragm
#surgicalcriticalcare
#gastroenterology
Reference:
Korn O, Oñate JC, López R (2007). "Anatomy of the Boerhaave syndrome". Surgery 141 (2): 222–8.
Labels:
Gastroenterology,
surgical critical care
Saturday, October 20, 2018
Donor liver temperature regulation
Q: Preferably liver should be maintained for transplant outside the body at (select one)
A) Body temperature
B) Ice cold temperature
Answer: A
Donated livers are usually kept in ice-cold temperature up to 12 hours till it gets transplanted as beyond this time period viability of transplanted liver may get affected. Endeavors are underway to keep donated livers at body like environment to increase the preservation time up to 24 hours. This technique is called "normothermic preservation". Besides keeping the liver at body temperature it also nourishes it with a continuous flow of nutrients.
#hepatology
#transplantation
Reference:
David Nasralla, Constantin C. Coussios. A randomized trial of normothermic preservation in liver transplantation, the Consortium for Organ Preservation in Europe. Nature volume 557, pages 50–56 (2018) Published: 18 April 2018
Friday, October 19, 2018
Methylene blue
Q: Methylene blue (MB) should be given with caution in patients with
A) Pulmonary hypertension
B) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
C) Severe liver insufficiency
D) On serotonergic agents
E) All of the above
Answer: E
Use of Methylene blue has seen a surge in recent years in critical patients in a quest to quickly blunt refractory vasoplegia. But it should be given with caution and history and concomitant use of other drugs should be taken into consideration. Most commonly missed is the use of SSRIs by patients who receive MB.
In patients with G6PD-deficiency, methylene blue catalyzes the oxidation of ferrous iron in hemoglobin to ferric iron causing paradoxical methemoglobinemia and hemolysis.
#pharmacology
#cardiovascular
References:
Gillman P.K. (October 2006). "Methylene blue implicated in potentially fatal serotonin toxicity". Anaesthesia. 61 (10): 1013–4.
Sikka P, Bindra VK, Kapoor S, Jain V, Saxena KK. Blue cures blue but be cautious. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences. 2011;3(4):543-545. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.90112.
A) Pulmonary hypertension
B) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
C) Severe liver insufficiency
D) On serotonergic agents
E) All of the above
Answer: E
Use of Methylene blue has seen a surge in recent years in critical patients in a quest to quickly blunt refractory vasoplegia. But it should be given with caution and history and concomitant use of other drugs should be taken into consideration. Most commonly missed is the use of SSRIs by patients who receive MB.
In patients with G6PD-deficiency, methylene blue catalyzes the oxidation of ferrous iron in hemoglobin to ferric iron causing paradoxical methemoglobinemia and hemolysis.
#pharmacology
#cardiovascular
References:
Gillman P.K. (October 2006). "Methylene blue implicated in potentially fatal serotonin toxicity". Anaesthesia. 61 (10): 1013–4.
Sikka P, Bindra VK, Kapoor S, Jain V, Saxena KK. Blue cures blue but be cautious. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences. 2011;3(4):543-545. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.90112.
Thursday, October 18, 2018
Warfarin overdose
Q: All of the following are useful in Warfarin overdose except?
A) PCC (Prothrombin complex concentrates) (3- or 4-factor)
B) Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
C) Vitamin K
D) Hemodialysis (HD)
E) Cholestyramine
Answer: D
There are two objectives for this question. First is to emphasize that HD has no role in warfarin toxicity. Second, Cholestyramine may have some role in enhancing the elimination of warfarin in early period from the gastrointestinal(GI) tract.
All other are well know treatments of warfarin overdose.
#Toxicology
References;
Jähnchen E, Meinertz T, Gilfrich HJ, et al. Enhanced elimination of warfarin during treatment with cholestyramine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1978; 5:437.
Renowden S, Westmoreland D, White JP, Routledge PA. Oral cholestyramine increases elimination of warfarin after overdose. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985; 291:513.
A) PCC (Prothrombin complex concentrates) (3- or 4-factor)
B) Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
C) Vitamin K
D) Hemodialysis (HD)
E) Cholestyramine
Answer: D
There are two objectives for this question. First is to emphasize that HD has no role in warfarin toxicity. Second, Cholestyramine may have some role in enhancing the elimination of warfarin in early period from the gastrointestinal(GI) tract.
All other are well know treatments of warfarin overdose.
#Toxicology
References;
Jähnchen E, Meinertz T, Gilfrich HJ, et al. Enhanced elimination of warfarin during treatment with cholestyramine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1978; 5:437.
Renowden S, Westmoreland D, White JP, Routledge PA. Oral cholestyramine increases elimination of warfarin after overdose. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985; 291:513.
Wednesday, October 17, 2018
EKG changes in hypothyroidism
Q: Pericarditis in hypothyroidism fails to produce diffuse ST- and T-wave elevations on EKG. What is the probable cause?
Answer:
Pericarditis in hypothyroidism fails to produce diffuse ST and T-wave elevations on EKG due to low voltage. Other changes which can be noted on EKG in hypothyroidism include bradycardia, prolonged QTc, and atrioventricular blocks.
#cardiology
#endocrinology
References:
1. Kudo Y, Yamasaki F, Doi T, et al. Clinical significance of low voltage in asymptomatic patients with pericardial effusion free of heart disease. Chest 2003; 124:2064.
2. Patil VC, Patil HV, Agrawal V, Patil S. Cardiac tamponade in a patient with primary hypothyroidism. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011;15(Suppl2):S144–S146.
Answer:
Pericarditis in hypothyroidism fails to produce diffuse ST and T-wave elevations on EKG due to low voltage. Other changes which can be noted on EKG in hypothyroidism include bradycardia, prolonged QTc, and atrioventricular blocks.
#cardiology
#endocrinology
References:
1. Kudo Y, Yamasaki F, Doi T, et al. Clinical significance of low voltage in asymptomatic patients with pericardial effusion free of heart disease. Chest 2003; 124:2064.
2. Patil VC, Patil HV, Agrawal V, Patil S. Cardiac tamponade in a patient with primary hypothyroidism. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011;15(Suppl2):S144–S146.
Labels:
cardiology,
endocrinology and metabolism
Tuesday, October 16, 2018
"alarm clock" headache
Q: What is a Hypnic headache or an "alarm clock" headache?
Answer: a Hypnic headache is relatively an uncommon headache which may be benign but possibly a manifestation of an underlying tumor, particularly if occurs in later part of the life. It is called an "alarm clock" headache, as it happens only during the sleep and awaken the patient from sleep and persists for from 15 minutes to 3 hours. It exclusively never happens during the daytime. MRI is recommended to rule out any underlying tumor.
#neurology
References:
1. Holle D, Naegel S, Obermann M. Hypnic headache. Cephalalgia 2013; 33:1349.
2. Holle D, Naegel S, Obermann M. Pathophysiology of hypnic headache. Cephalalgia 2014; 34:806.
3. Liang JF, Wang SJ. Hypnic headache: a review of clinical features, therapeutic options and outcomes. Cephalalgia 2014; 34:795.
Answer: a Hypnic headache is relatively an uncommon headache which may be benign but possibly a manifestation of an underlying tumor, particularly if occurs in later part of the life. It is called an "alarm clock" headache, as it happens only during the sleep and awaken the patient from sleep and persists for from 15 minutes to 3 hours. It exclusively never happens during the daytime. MRI is recommended to rule out any underlying tumor.
#neurology
References:
1. Holle D, Naegel S, Obermann M. Hypnic headache. Cephalalgia 2013; 33:1349.
2. Holle D, Naegel S, Obermann M. Pathophysiology of hypnic headache. Cephalalgia 2014; 34:806.
3. Liang JF, Wang SJ. Hypnic headache: a review of clinical features, therapeutic options and outcomes. Cephalalgia 2014; 34:795.
Monday, October 15, 2018
Infusion rate of Platelets
Q: How quickly one apheresis unit of platelets (six units of pooled platelets) can be transfused?
Answer: About 20 to 30 minutes
Although platelets transfusion can be achieved within half hour of its availability, two factors should be taken into consideration. First, the predisposition of a patient to develop TACO (transfusion-associated circulatory overload ) and a patient's body size. Said that it is recommended that all platelet transfusions should be completed within four hours after they leave the blood bank.
#hematology
References:
1. Slichter SJ. Platelet transfusion therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2007; 21:697.
2. McCullough J. Overview of platelet transfusion. Semin Hematol 2010; 47:235.
3. Alam A, Lin Y, Lima A, et al. The prevention of transfusion-associated circulatory overload. Transfus Med Rev 2013; 27:105.
Answer: About 20 to 30 minutes
Although platelets transfusion can be achieved within half hour of its availability, two factors should be taken into consideration. First, the predisposition of a patient to develop TACO (transfusion-associated circulatory overload ) and a patient's body size. Said that it is recommended that all platelet transfusions should be completed within four hours after they leave the blood bank.
#hematology
References:
1. Slichter SJ. Platelet transfusion therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2007; 21:697.
2. McCullough J. Overview of platelet transfusion. Semin Hematol 2010; 47:235.
3. Alam A, Lin Y, Lima A, et al. The prevention of transfusion-associated circulatory overload. Transfus Med Rev 2013; 27:105.
Sunday, October 14, 2018
Hypokalemia in Severe Diarrhea
Q: What are the two mechanisms causing hypokalemia in severe diarrhea?
Answer: The objective of the above question is to describe a less known reason of hypokalemia in severe diarrhea. Besides the loss of potassium in the diarrheal fluid, hypovolemia-induced secondary hyperaldosteronism also contributes to hypokalemia by increasing colonic potassium secretion.
#electrolytes
#Gastroenterology
#endocrinology
Reference:
Corry DB, Tuck ML. Secondary aldosteronism.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1995 Sep;24(3):511-29.
Answer: The objective of the above question is to describe a less known reason of hypokalemia in severe diarrhea. Besides the loss of potassium in the diarrheal fluid, hypovolemia-induced secondary hyperaldosteronism also contributes to hypokalemia by increasing colonic potassium secretion.
#electrolytes
#Gastroenterology
#endocrinology
Reference:
Corry DB, Tuck ML. Secondary aldosteronism.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1995 Sep;24(3):511-29.
Saturday, October 13, 2018
Epitrochlear Lymph-Nodes
Q: The epitrochlear lymph nodes are usually palpable at? (select one)
A) Medial side of the arm below the elbow
B) Lateral side of the arm below the elbow
C) Medial side of the arm above the elbow
B) Lateral side of the arm above the elbow
E) At antecubital fossa
Answer: A
Epitrochlear lymph nodes are if palpable, are usually at the medial side of the arm below the elbow. The objective of the above question is to highlight the fact that if epitrochlear lymph nodes are palpable, they are always pathologic. Underlying causes include localized infection, lymphoma, sarcoidosis, tularemia, and secondary syphilis.
#physicalexam
#oncology
#infectiousdisease
References:
1. Yardimci VH, Yardimci AH. An Unusual First Manifestation of Hodgkin Lymphoma: Epitrochlear Lymph Node İnvolvement—A Case Report and Brief Review of Literature. Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case Reports. 2017;5(2):2324709
2. Catalano O, Nunziata A, Saturnino PP, Siani A. Epitrochlear lymph nodes: Anatomy, clinical aspects, and sonography features. Pictorial essay. Journal of Ultrasound. 2010;13(4):168-174.
A) Medial side of the arm below the elbow
B) Lateral side of the arm below the elbow
C) Medial side of the arm above the elbow
B) Lateral side of the arm above the elbow
E) At antecubital fossa
Answer: A
Epitrochlear lymph nodes are if palpable, are usually at the medial side of the arm below the elbow. The objective of the above question is to highlight the fact that if epitrochlear lymph nodes are palpable, they are always pathologic. Underlying causes include localized infection, lymphoma, sarcoidosis, tularemia, and secondary syphilis.
#physicalexam
#oncology
#infectiousdisease
References:
1. Yardimci VH, Yardimci AH. An Unusual First Manifestation of Hodgkin Lymphoma: Epitrochlear Lymph Node İnvolvement—A Case Report and Brief Review of Literature. Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case Reports. 2017;5(2):2324709
2. Catalano O, Nunziata A, Saturnino PP, Siani A. Epitrochlear lymph nodes: Anatomy, clinical aspects, and sonography features. Pictorial essay. Journal of Ultrasound. 2010;13(4):168-174.
Thursday, October 11, 2018
Drug Induced Pseudo-Lymphoma
Q: Which of the following drug may cause pseudo-lymphoma?
A) Atenolol
B) Captopril
C) Cephalosporins
D) Phenytoin
E) Hydralazine
Answer: D
Lymphadenopathy associated with hydantoin derivatives drugs is well known for almost 80 years. On biopsy, it is manifested as a benign lymphoid follicular hyperplasia. Clinically, it may present as fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, eosinophilia, and hepatitis. Usually, it gets resolved by the discontinuation of the drug but if symptoms persist, steroids may be helpful.
#pharmacology
#oncology
Reference:
Johns ME, Moscinski LC, Sokol L. Phenytoin-Associated Lymphoadenopathy Mimicking a Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma. Mediterranean Journal of Hematology and Infectious Diseases. 2010;2(2):e2010028.
A) Atenolol
B) Captopril
C) Cephalosporins
D) Phenytoin
E) Hydralazine
Answer: D
Lymphadenopathy associated with hydantoin derivatives drugs is well known for almost 80 years. On biopsy, it is manifested as a benign lymphoid follicular hyperplasia. Clinically, it may present as fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, eosinophilia, and hepatitis. Usually, it gets resolved by the discontinuation of the drug but if symptoms persist, steroids may be helpful.
#pharmacology
#oncology
Reference:
Johns ME, Moscinski LC, Sokol L. Phenytoin-Associated Lymphoadenopathy Mimicking a Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma. Mediterranean Journal of Hematology and Infectious Diseases. 2010;2(2):e2010028.
Wednesday, October 10, 2018
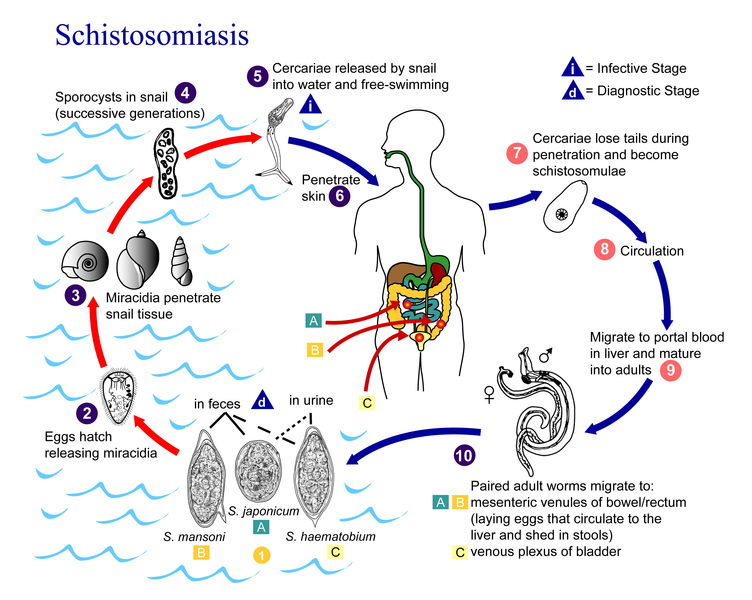
Corticosteroids in Schistosomiasis
Q: 52 year old male, who returned from Zambia 8 weeks ago, is admitted to ICU with fever, malaise, hypotension, generalized urticaria and pruritic rash. Blood workup showed marked eosinophilia. Infectious Disease service is consulted and they strongly suspect Schistosomiasis. While urine and fecal microbiology, as well as PCR, is awaiting, infectious disease services recommend a single dose treatment of Schistosomiasis with Praziquantel. Also, corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce inflammation. What should watch out?
Answer: A cure rate of 60-90% is described after a single dose treatment with praziquantel. But two things should be watched out.
1. Maturing schistosomes are less susceptible to therapy than adult worms, the second course of treatment may be required after few weeks.
2. Corticosteroids may affect the plasma levels of Praziquantel. So patient should be watched for the possible requirement of the second dose.
#infectiousdiseases
#pharmacology
References:
1. Grandière-Pérez L, Ansart S, Paris L, et al. Efficacy of praziquantel during the incubation and invasive phase of Schistosoma haematobium schistosomiasis in 18 travelers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006; 74:814. 2.
Vazquez ML, Jung H, Sotelo J. Plasma levels of praziquantel decrease when dexamethasone is given simultaneously. Neurology 1987; 37:1561.
3. Ross AG, Bartley PB, Sleigh AC, et al. Schistosomiasis. N Engl J Med 2002; 346:1212.
Answer: A cure rate of 60-90% is described after a single dose treatment with praziquantel. But two things should be watched out.
1. Maturing schistosomes are less susceptible to therapy than adult worms, the second course of treatment may be required after few weeks.
2. Corticosteroids may affect the plasma levels of Praziquantel. So patient should be watched for the possible requirement of the second dose.
#infectiousdiseases
#pharmacology
References:
1. Grandière-Pérez L, Ansart S, Paris L, et al. Efficacy of praziquantel during the incubation and invasive phase of Schistosoma haematobium schistosomiasis in 18 travelers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006; 74:814. 2.
Vazquez ML, Jung H, Sotelo J. Plasma levels of praziquantel decrease when dexamethasone is given simultaneously. Neurology 1987; 37:1561.
3. Ross AG, Bartley PB, Sleigh AC, et al. Schistosomiasis. N Engl J Med 2002; 346:1212.
Tuesday, October 9, 2018
Intravenous Lipid Emulsion therapy and laboratory measurements
Q: 54-year-old male is admitted to ICU with calcium channel blocker overdose. A decision has been made to start Intravenous Lipid Emulsion (ILE therapy) due to the failure of conventional antidotes and hemodynamic instability. All of the following laboratory measurement may get effected except?
A) serum magnesium
B) serum creatinine
C) serum lipase
D) serum potassium
E) all of the above
Answer: D
As expected ILE therapy interferes with most laboratory measurements of electrolytes and drug levels. Interestingly, it does not affect two important lab measurements frequently used in ICU, potassium, and troponin-I.
#electrolytes
#toxicology
References:
Grunbaum AM, Gilfix BM, Gosselin S, Blank DW. Analytical interferences resulting from intravenous lipid emulsion. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2012; 50:812.
A) serum magnesium
B) serum creatinine
C) serum lipase
D) serum potassium
E) all of the above
Answer: D
As expected ILE therapy interferes with most laboratory measurements of electrolytes and drug levels. Interestingly, it does not affect two important lab measurements frequently used in ICU, potassium, and troponin-I.
#electrolytes
#toxicology
References:
Grunbaum AM, Gilfix BM, Gosselin S, Blank DW. Analytical interferences resulting from intravenous lipid emulsion. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2012; 50:812.
Labels:
electrolytes and acid base,
toxicology
Monday, October 8, 2018
CVP waveform
Q: Which of the following statement is false regarding "Central Venous Pressure" (CVP)?
A) a wave is due to the increased atrial pressure during right atrial contraction.
B) c wave is due to a slight elevation of the mitral valve during early ventricular contraction.
C) x descent is caused by the downward movement of the right ventricle during systole.
D) v wave arises when the blood fills up the right atrium against a closed tricuspid valve.
E) y descent is produced by the tricuspid valve opening in the diastole.
Answer: B
CVP is directly produced due to the cardiac function on the right side of the heart.
B is a wrong answer as the mitral valve has no direct contribution to the CVP wave, despite CVP is a good measurement of left ventricular function. Mitral valve lies on the left side between the left atrium and left ventricle. Instead, it's a tricuspid valve slight elevation during early ventricular systole which produces c wave.
CVP is consist of 3 waves (a, c and v) and 2 descents (x and y)
All other choices are correct!
#cardiology
Reference:
Drazner MH, Rame JE, Dries DL. Third heart sound and elevated jugular venous pressure as markers of the subsequent development of heart failure in patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Am J Med 2003; 114:431.
A) a wave is due to the increased atrial pressure during right atrial contraction.
B) c wave is due to a slight elevation of the mitral valve during early ventricular contraction.
C) x descent is caused by the downward movement of the right ventricle during systole.
D) v wave arises when the blood fills up the right atrium against a closed tricuspid valve.
E) y descent is produced by the tricuspid valve opening in the diastole.
Answer: B
CVP is directly produced due to the cardiac function on the right side of the heart.
B is a wrong answer as the mitral valve has no direct contribution to the CVP wave, despite CVP is a good measurement of left ventricular function. Mitral valve lies on the left side between the left atrium and left ventricle. Instead, it's a tricuspid valve slight elevation during early ventricular systole which produces c wave.
CVP is consist of 3 waves (a, c and v) and 2 descents (x and y)
All other choices are correct!
#cardiology
Reference:
Drazner MH, Rame JE, Dries DL. Third heart sound and elevated jugular venous pressure as markers of the subsequent development of heart failure in patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Am J Med 2003; 114:431.
Sunday, October 7, 2018
Rash of Fat Embolism
Q: Rash associated with Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES) usually occurs on the nondependent regions of the body? (select one)
A) True
B) False
Answer: A
The classic pathognomic red-brown petechial rash of FES occurs between 24 to 72 hours after long bone trauma. Characteristically, it occurs on the nondependent regions of the body i.e. head, neck, anterior thorax, axillae, and sub-conjunctiva. FES is a clinical diagnosis so the physical exam is of utmost importance. 1
#trauma
#surgicalcriticalcare
References:
A) True
B) False
Answer: A
The classic pathognomic red-brown petechial rash of FES occurs between 24 to 72 hours after long bone trauma. Characteristically, it occurs on the nondependent regions of the body i.e. head, neck, anterior thorax, axillae, and sub-conjunctiva. FES is a clinical diagnosis so the physical exam is of utmost importance. 1
#trauma
#surgicalcriticalcare
References:
1. Georgopoulos D, Bouros D. Fat embolism syndrome: clinical examination is still the preferable diagnostic method. Chest 2003; 123:982.
2. Kaplan RP, Grant JN, Kaufman AJ. Dermatologic features of the fat embolism syndrome. Cutis 1986; 38:52.
Saturday, October 6, 2018
Uremic frost
Q: What is Uremic frost?
Answer: Uremic frost is a dermatological manifestation of severe azotemia. When blood urea nitrogen level is high, the concentration of urea in sweat increases greatly. Evaporation of sweat with high urea concentration causes urea to crystallize and get deposited on the skin.
#Nephrology
Reference:
Mohit Mathur Amith V.L. D'Souza Vinay Malhotra Dhananjai Agarwal Pankaj Beniwal - Uremic frost. Clinical Kidney Journal, Volume 7, Issue 4, 1 August 2014, Pages 418–419
#Nephrology
Reference:
Mohit Mathur Amith V.L. D'Souza Vinay Malhotra Dhananjai Agarwal Pankaj Beniwal - Uremic frost. Clinical Kidney Journal, Volume 7, Issue 4, 1 August 2014, Pages 418–419
Friday, October 5, 2018
Antibiotic for pruritus associated with cholestasis
Q: Which of the following antibiotic has shown benefit in pruritis associated with cholestasis?
A) Cefepime
B) Ceftriaxone
C) Ciprofloxacine
D) Rifampin
E) Meropenem
Answer: D
Rifampin is a potent agonist of the pregnane X receptor, a mediator for various detoxification and hepatobiliary processes. This gives rifampin a unique advantage among all antibiotics as an antipruritic agent. But rifampin itself can cause increased liver enzymes so it should be used only if needed as an alternative agent.
#hepatology
#pharmacology
References:
1. Podesta A, Lopez P, Terg R, et al. Treatment of pruritus of primary biliary cirrhosis with rifampin. Dig Dis Sci 1991; 36:216.
2. Ghent CN, Carruthers SG. Treatment of pruritus in primary biliary cirrhosis with rifampin. Results of a double-blind, crossover, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 1988; 94:488.
3. Khurana S, Singh P. Rifampin is safe for treatment of pruritus due to chronic cholestasis: a meta-analysis of prospective randomized-controlled trials. Liver Int 2006; 26:943.
A) Cefepime
B) Ceftriaxone
C) Ciprofloxacine
D) Rifampin
E) Meropenem
Answer: D
Rifampin is a potent agonist of the pregnane X receptor, a mediator for various detoxification and hepatobiliary processes. This gives rifampin a unique advantage among all antibiotics as an antipruritic agent. But rifampin itself can cause increased liver enzymes so it should be used only if needed as an alternative agent.
#hepatology
#pharmacology
References:
1. Podesta A, Lopez P, Terg R, et al. Treatment of pruritus of primary biliary cirrhosis with rifampin. Dig Dis Sci 1991; 36:216.
2. Ghent CN, Carruthers SG. Treatment of pruritus in primary biliary cirrhosis with rifampin. Results of a double-blind, crossover, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 1988; 94:488.
3. Khurana S, Singh P. Rifampin is safe for treatment of pruritus due to chronic cholestasis: a meta-analysis of prospective randomized-controlled trials. Liver Int 2006; 26:943.
Thursday, October 4, 2018
Types of Hepatorenal syndrome
Q: Which of the hepatorenal syndrome is considered more serious? (select one)
A) Type 1
B) Type 2
Answer: A
Hepatorenal Syndrome is classified into Type 1 and Type 2 on the basis of the rapidity of the decline of renal function, and clinical signs.
Type 1 is considered more serious as decline happens quickly with oliguria and rise in creatinine within 10-14 days.
Type 2 is a slow and insidious process marked by the ascites which is resistant to diuretics.
#nephrology
#hepatology
References:
Arroyo V, Ginès P, Gerbes AL, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology 1996; 23:164.
Ginès P, Schrier RW. Renal failure in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2009; 361:1279.
A) Type 1
B) Type 2
Answer: A
Hepatorenal Syndrome is classified into Type 1 and Type 2 on the basis of the rapidity of the decline of renal function, and clinical signs.
Type 1 is considered more serious as decline happens quickly with oliguria and rise in creatinine within 10-14 days.
Type 2 is a slow and insidious process marked by the ascites which is resistant to diuretics.
#nephrology
#hepatology
References:
Arroyo V, Ginès P, Gerbes AL, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology 1996; 23:164.
Ginès P, Schrier RW. Renal failure in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2009; 361:1279.
Wednesday, October 3, 2018
Atelectasis in pilots
Q: 32-year-old professional pilot is admitted to ICU after he required intubation in the field after he performed some quick maneuverings during a practice session. Bedside CXR showed various sites of collapse on bilateral lungs. What kind of atelectasis is suspected?
Answer: Acceleration Atelectasis
There are at least eight types of non-obstructive atelectasis
Answer: Acceleration Atelectasis
There are at least eight types of non-obstructive atelectasis
- Relaxation
- Compressive
- Adhesive
- Cicatrization
- Replacement
- Acceleration
- Rounded
- Plate-like
Definitions/details of above atelectasis can be found at reference below. 1
Acceleration atelectasis is unique in the sense that it occurs in professional pilots who get engaged to very high, vertical accelerative forces at or above 5G. Airways get distorted and closed at 5G due to gravitational forces. Also, the atelectasis gets exacerbated by a high fractional concentration of oxygen on board.
#pulmonary
References:
1. Woodring JH, Reed JC. Types and mechanisms of pulmonary atelectasis. J Thorac Imaging 1996; 11:92.
2. Tacker WA Jr, Balldin UI, Burton RR, et al. Induction and prevention of acceleration atelectasis. Aviat Space Environ Med 1987; 58:69.
#pulmonary
References:
1. Woodring JH, Reed JC. Types and mechanisms of pulmonary atelectasis. J Thorac Imaging 1996; 11:92.
2. Tacker WA Jr, Balldin UI, Burton RR, et al. Induction and prevention of acceleration atelectasis. Aviat Space Environ Med 1987; 58:69.
Tuesday, October 2, 2018
Bentall Procedure
Q: 52 years old male is admitted to ICU with shortness of breath. The patient was discharged just one week ago after successful Bentall procedure. What is Bentall Procedure?
Answer: Composite graft replacement of the aortic valve, aortic root and ascending aorta, with re-implantation of the coronary arteries into the graft is called a Bentall procedure. This surgery is to treat combined aortic valve and ascending aorta disease. It is described almost 50 years ago.
The figure below shows before (a) and after (b)
The figure below shows before (a) and after (b)

Reference:
Monday, October 1, 2018
Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis
Q: All of the following is the part of LRINEC score except?
A) C-reactive protein
B) Hemoglobin
C) Glucose
D) Potassium
E) Creatinine
Answer: D
The LRINEC is a "Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis" score. It is a helpful tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. An LRINEC Score of more than 6 was found to have a positive predictive value of 92% and a negative predictive value of 96%.
Score calculator can be found online.
It consists of
#surgicalcriticalcare
#infectiousdiseases
Reference:
Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32(7):1535-1541.
A) C-reactive protein
B) Hemoglobin
C) Glucose
D) Potassium
E) Creatinine
Answer: D
The LRINEC is a "Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis" score. It is a helpful tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. An LRINEC Score of more than 6 was found to have a positive predictive value of 92% and a negative predictive value of 96%.
Score calculator can be found online.
It consists of
- C-reactive protein
- Hemoglobin
- Glucose
- Sodium
- Creatinine, and
- White Blood Cell (WBC) count
#surgicalcriticalcare
#infectiousdiseases
Reference:
Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32(7):1535-1541.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)